Eno Taylor
Effect of Sacubitril-Valsartan on Patient Reported Health Status in an Advanced Heart Failure Clinic
April 21, 2020 in College of Pharmacy, Virtual Poster Session Spring 2020
ABSTRACT
Background
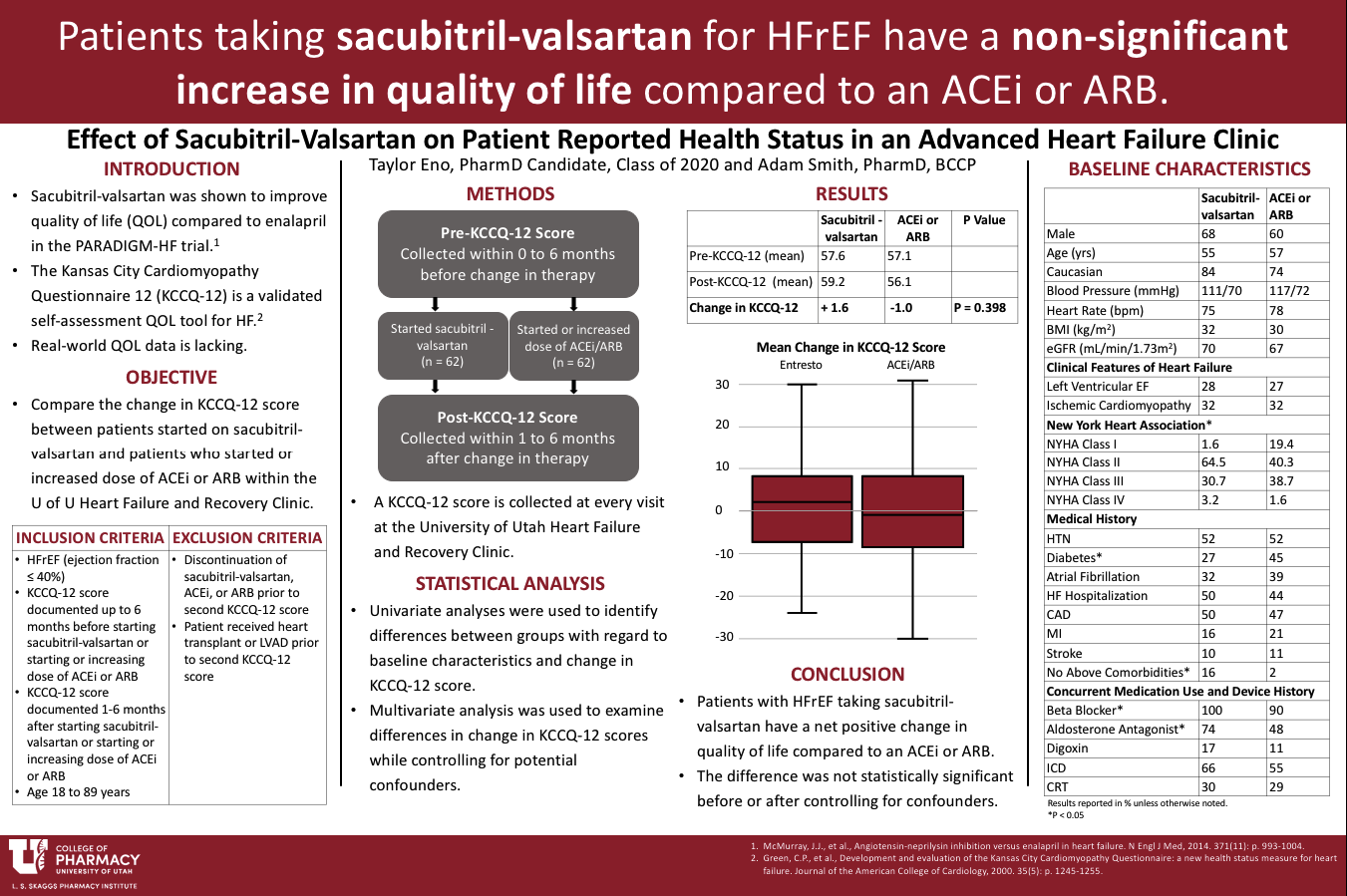
Quality of life (QOL) is reduced in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF). The Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire 12 (KCCQ-12) is a validated self-assessment QOL tool for HFrEF. Sacubitril-valsartan was shown to statistically improve QOL when compared to enalapril in the PARADIGM-HF (Prospective Comparison of ARNI with ACE inhibitor to Determine Impact on Global Mortality and Morbidity in Heart Failure) trial. Real-world data is limited.
Objective
This study compared changes in KCCQ-12 score between patients started on sacubitril-valsartan and patients who started or increased dose of ACEi or ARB within the University of Utah Heart Failure and Recovery Clinic from January 1, 2016 to December 31, 2018.
Methods
Patients prescribed sacubitril-valsartan or who started/increased their dose of ACEi or ARB, with left ventricular ejection fraction ≤40% were identified. Included patients have a KCCQ-12 score recorded 0-6 months prior to and 1-6 months after the therapy change. Patient characteristics were obtained through chart review. The primary outcome is change in KCCQ-12 score. Regression analysis was used to determine if any variables affected the outcome.
Results
The mean change in KCCQ-12 score for the sacubitril-valsartan and the ACEi/ARB group was 1.6 and -1.0, respectively (p = 0.40). After controlling for differences in baseline characteristics and clinically relevant variables in a multivariate regression, there was no significant difference in KCCQ-12 between the two groups.
Conclusions
Patients starting sacubitril-valsartan had a non-significant increase in KCCQ-12 score when compared to patients that started/increased an ACEi or ARB.
