Chambers Cole
Assessment of Current Asthma Self-Management Education Practices Within Utah Pharmacies: A Qualitative Study
April 28, 2020 in College of Pharmacy, Virtual Poster Session Spring 2020
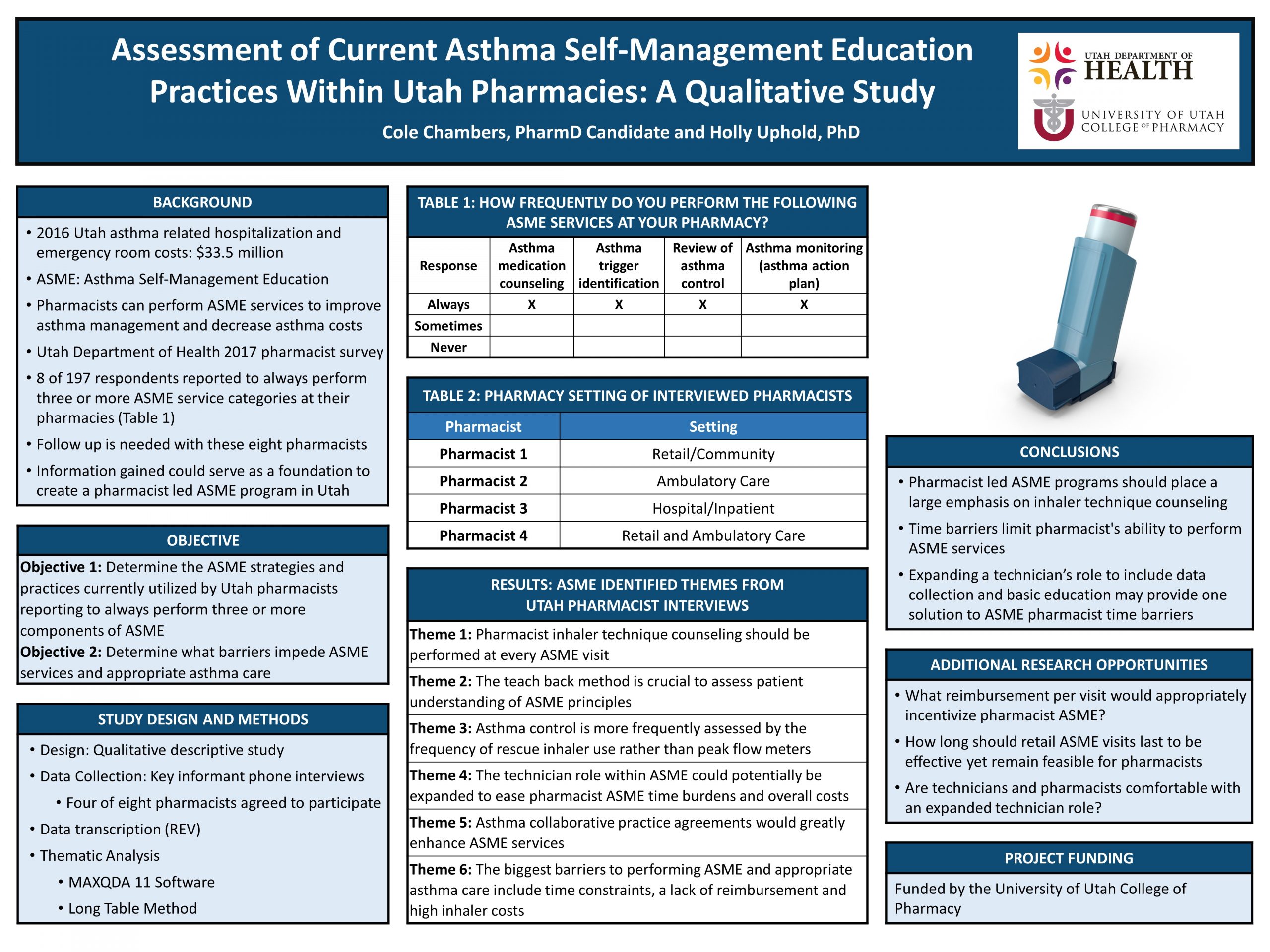
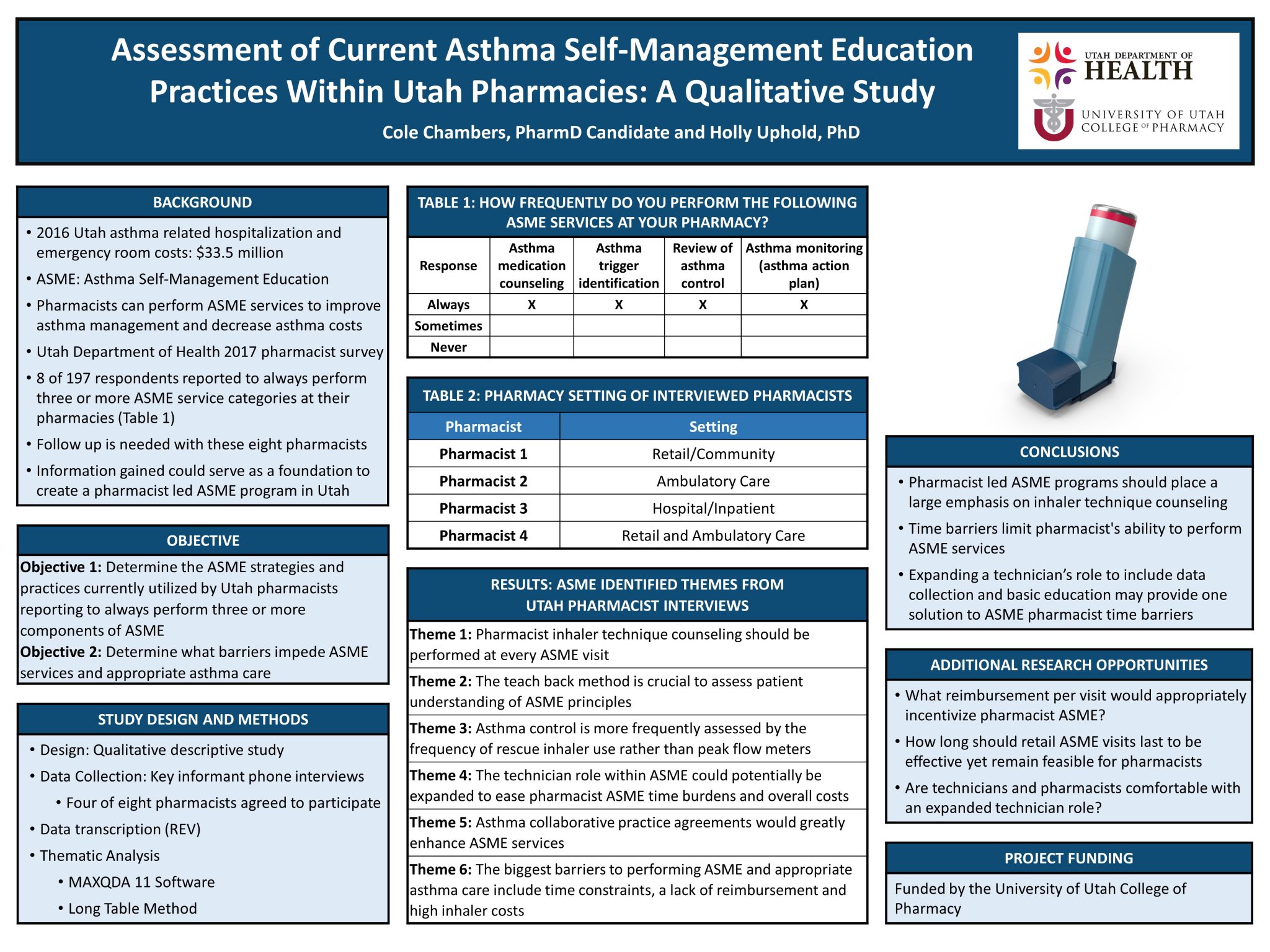
Purpose: Asthma self-management education (ASME) is a fundamental component of asthma management that improves asthma outcomes and generates cost savings related to a reduction in unnecessary health care use. Pharmacists can play a key role in providing ASME services and improving asthma outcomes for their patients. Key informant interviews were conducted with pharmacists performing ASME services within Utah pharmacies. This allowed us to better understand what ASME practices are currently used within the state. These findings will be used to further evaluate and improve Utah ASME strategies in addition to providing a foundation for a future pharmacist-led ASME program.
Methods: Key informant interviews were performed with eight Utah pharmacists who reported to regularly provide ASME services. Interview questions focused on ASME methods, reimbursement incentives and barriers. Interview audio was transcribed and then analyzed thematically using a qualitative descriptive approach.
Results: Five common themes were identified as critical components of ASME practices, including: the importance of inhaler counseling at every visit, the importance of the teach back method to assess patient understanding, widespread pharmacist use of rescue inhaler usage to assess asthma control, the importance of collaborative practice agreements within ASME, and the potential use and expanded role of pharmacy technicians within ASME. Barriers to ASME services included time, lack of reimbursement, and high inhaler costs.
Conclusion: This study identified several key strategies for pharmacists to perform effective and feasible ASME. Future ASME programs should focus on incorporating components of inhaler technique counseling while maximizing the role of pharmacy technicians to overcome ASME time barriers.